SOURCES OF INDIAN CONSTITUTION
The Constitution of India is the backbone of democracy in our country that came into existence on 26th November 1949. The Indian Constitution has been formed by borrowing from all the major constitutions of the world;giving rise to various legal principles.
The Government of India Act of 1935:

This was an Act passed by the Parliament of Britain. It provided a framework for the government of India and was passed in the response to demands of the Indian leaders for democracy.
Those features our constitution has features taken from the Government of India Act, 1935 are:
- Federal Scheme
- Office of governor
- Judiciary
- Public Service Commissions
- Emergency provisions
- Administrative details
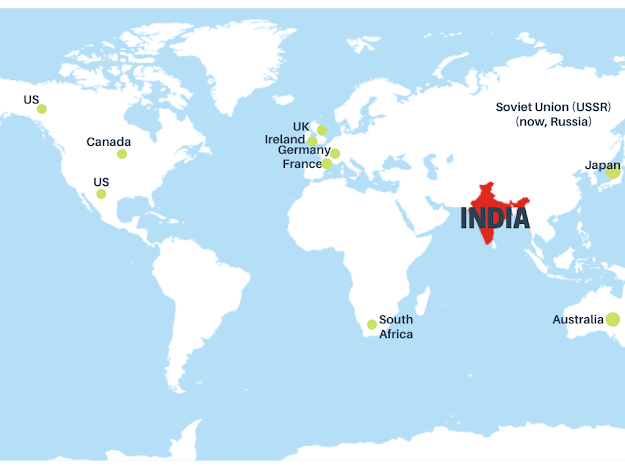
Australia:
- Concurrent list
- Freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse
- Joint-sitting of the two Houses of Parliament
Canada:

- Federation with a strong Centre
- Vesting of residuary powers in the Centre
- Appointment of state governors by the Centre
- Advisory jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
Ireland:
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Nomination of members to Rajya Sabha
- Method of election of the president
Japan:
- Procedure Established by law
Soviet Union (USSR) (now, Russia):
- Fundamental duties
- Ideal of justice (social, economic and political) in the Preamble
UK:
- Parliamentary government
- Rule of Law
- Legislative procedure
- Single Citizenship
- Cabinet system
- Prerogative writs
- Parliamentary privileges
- Bicameralism
US:
- Fundamental rights
- Independence of judiciary
- Impeachment of the president
- Removal of Supreme Court and High Court judges
- Post of vice-president
- Judicial Review
Germany (Weimar):

- Suspension of Fundamental Rights during emergency
South Africa:
- Republic
- Ideals of liberty, equality and fraternity in the Preamble
Though the Indian Constitution is a bulky borrowed bag it is not an exact copy or made any plagiarism as the borrowings have been justified and well defended by the constitution-makers. however, at the same time, the framers have also considered the following factors −
- Historical perspective of India;
- Geographical diversity of India; and
- Cultural and traditional characteristics of India.
For more details and notes please visit, share, follow and subscribe to the blog and youtube channel adityapedia. dont forget to like our fb page too. Its just a click away - absolutely FREE








No comments:
Post a Comment